 |
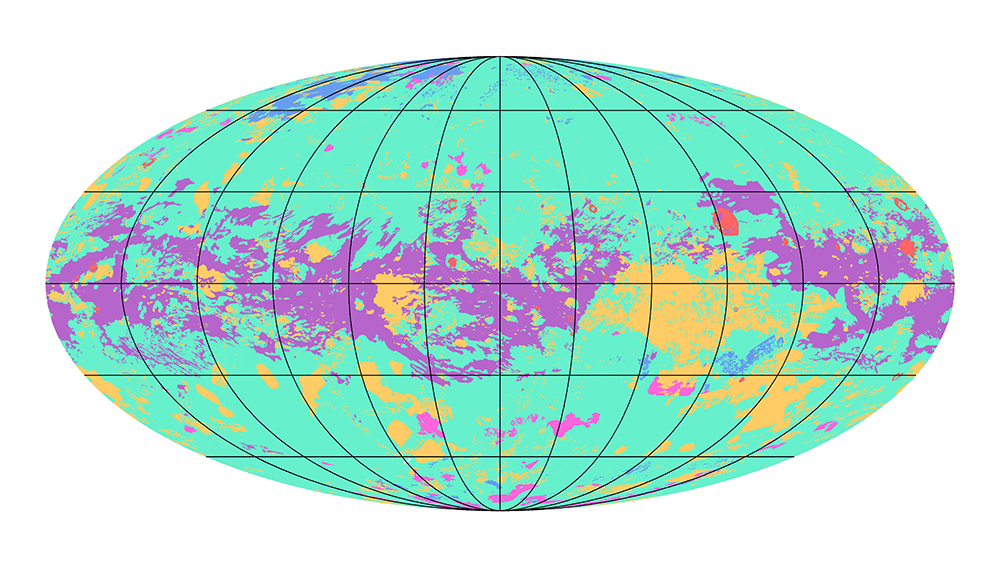
The first global geologic map of Saturn's largest moon, Titan.
(Image: © NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU)
|
A new geologic map of Saturn's large moon Titan reveals just how much liquid this world holds.
The new map is the first to show the global geology of Titan, allowing scientists to get a better understanding about how different regions of the moon interact with each other.
Titan is considered a good spot to learn more about how the Earth looked during the early days of our own planet, because the Mercury-sized moon has a liquid cycle (like Earth). It also holds complex organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life.
The liquid that flows on this moon is not water, but hydrocarbons such as methane and ethane. That's because Titan is so cold that these molecules flow as liquids, instead of ending up like gas as we experience here on Earth.
"Despite the different materials, temperatures and gravity fields between Earth and Titan, many surface features are similar between the two worlds and can be interpreted as being products of the same geologic processes," lead researcher Rosaly Lopes, a planetary geologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, said in a statement.
"The map shows that the different geologic terrains have a clear distribution with latitude, globally, and that some terrains cover far more area than others," Lopes added.
Lopes and her team obtained the map using data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn for 13 years and flew by Titan more than 120 times between 2004 and the mission's end in 2017. The map includes information from Cassini's radar instrument, which could probe below the thick, orange clouds of Titan to see lakes and flowing liquid at the surface. Cassini's visible and infrared instruments were also used for mapping in cases where they "saw" large geological features of Titan amid the haze.
The new map also heavily used the expertise of geologist David Williams at Arizona State University. He previously worked with radar images of Venus from NASA's Magellan mission, and developed a smaller-scale geologic map of Titan. The moon's hydrocarbons, he said in the same statement, "rain down on the surface, flow in streams and rivers, accumulate in lakes and seas, and evaporate into the atmosphere. It's quite an astounding world."
A paper based on the research was published Nov. 18 in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Elizabeth Howell
Source News
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.